
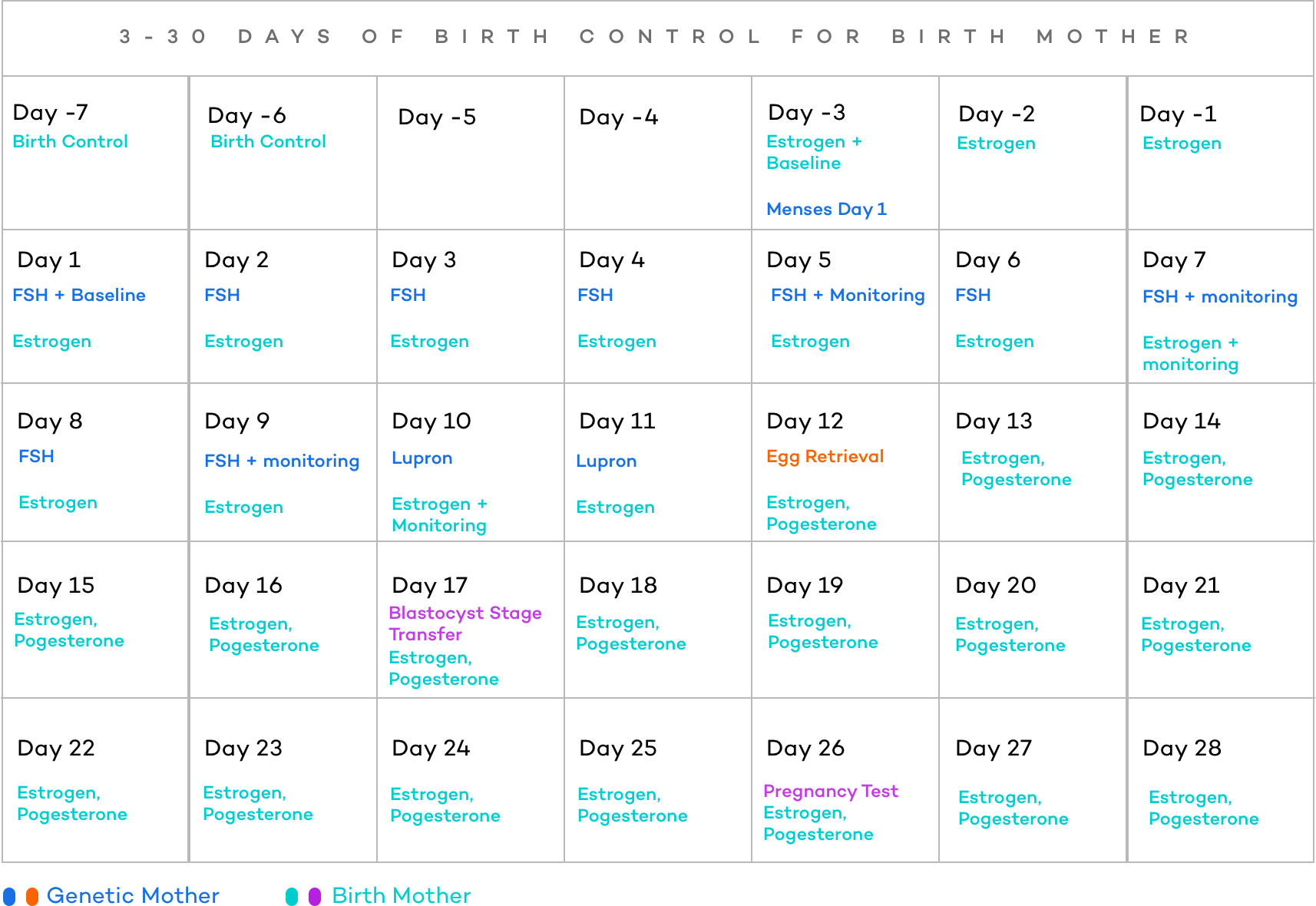
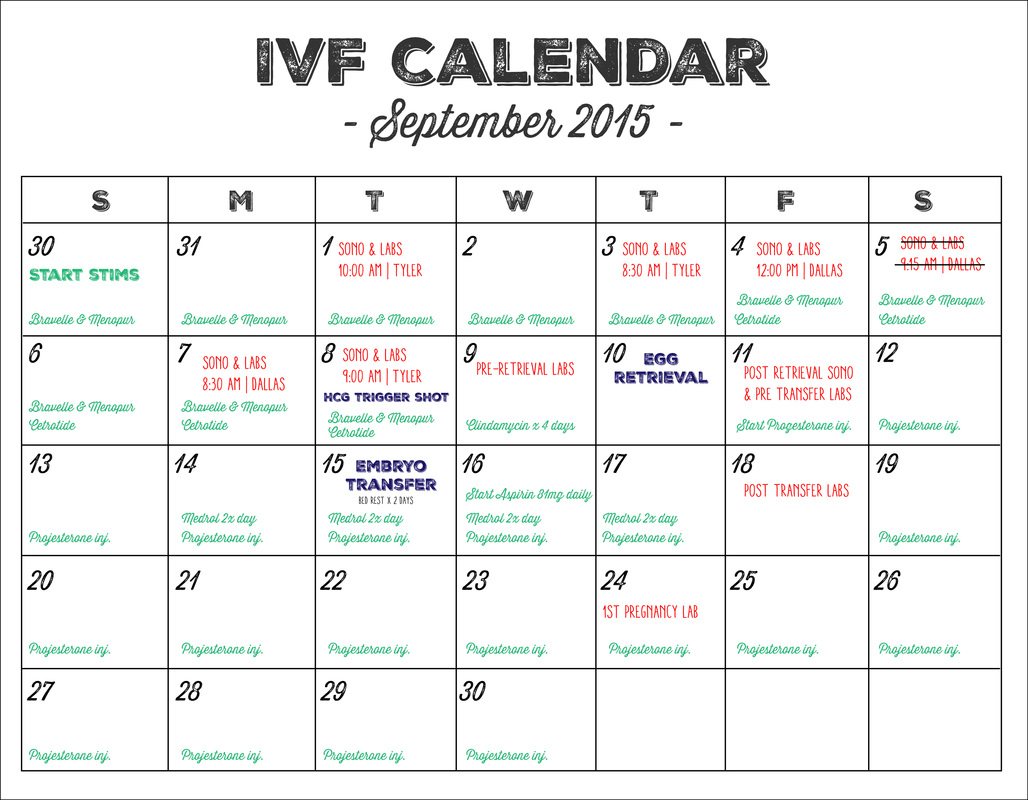
For example, lower quality embryos may entice your physician to compensate for the lower quality by transferring more than one embryo at a time. Typically, transfers consist of one embryo (at Day 5 of development, known as “ Blastocyst stage”), but there can be more, depending on what has been discussed previously and the specific circumstances. The goal is to limit the number of embryos transferred because they can result in multiple births. Physicians use a tool called “embryo grading” that helps to determine when to transfer and which embryos to transfer. Your fertility doctor will discuss with you the quality and quantity of embryos produced and outline exactly what the procedure involves. It doesn’t typically require any sedation or anesthesia. When it comes to the day of the embryo transfer, you can expect the procedure to be relatively straightforward. In this article, you’ll find out what to expect and what happens after the embryo transfer. It can also be a very emotional time for hopeful couples. After an embryo transfer, there can be many different symptoms.

The process involves transferring a fertilized egg into a woman’s uterus with the hope that it will implant and lead to a successful pregnancy. Embryo transfer is an outpatient procedure that does not typically require sedation and usually has no side effects.As part of an in-vitro fertilization (IVF) treatment, you will undergo an embryo transfer. Then, the patient's embryo(s) is thawed by Embryology Laboratory staff and transferred by the physician into the uterus. When the physician determines that the FET patient's endometrium is approaching its peak receptivity, the embryo transfer is scheduled. The patient’s menstrual cycle is closely monitored by blood tests and ultrasound in order to identify the optimal day for embryo transfer. Natural FETs require minimal or no medication. Our Center routinely performs "natural" FETs. In a medicated (also commonly referred to as a "programmed" FET), the patient takes a course of hormone medication that ensures that the patient's endometrium (lining of the uterus) is prepared to receive the thawed embryo(s). Furthermore, some FET patients may also take hormone medication to prepare for the transfer.Ībove: blastocyst prior to transfer The FET Process Medicated FET This process is called a frozen embryo transfer (FET).Ī patient preparing for an FET has blood tests and ultrasound monitoring in order for the physician to identify the optimal time in the patient's cycle to transfer the embryo(s). Previously cryopreserved embryo(s) are thawed and transferred into the patient’s uterus at the appropriate time in her menstrual cycle.
Advanced IVF Techniques Toggle Advanced IVF Techniques menu options.CRM's Pioneering Donor Egg Program Toggle CRM's Pioneering Donor Egg Program menu options.Ovulation Induction (OI) with Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) Toggle Ovulation Induction (OI) with Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) menu options.In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) Toggle In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) menu options.Treatments and Services Toggle Treatments and Services menu options.Administrative, Academic, Clinical Support and Research Staff Toggle Administrative, Academic, Clinical Support and Research Staff menu options.Psychological Services Toggle Psychological Services menu options.Ovulation Induction and IVF Nursing Staff.Nurses and Physician Assistants Toggle Nurses and Physician Assistants menu options.

Labs and Directors Toggle Labs and Directors menu options.Physicians Toggle Physicians menu options.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
